Titration is quantitative chemical analysis used in laboratories to find out the concentration of an identified analyte a substance to be analyzed. She completes the following steps as part of her titration procedure.
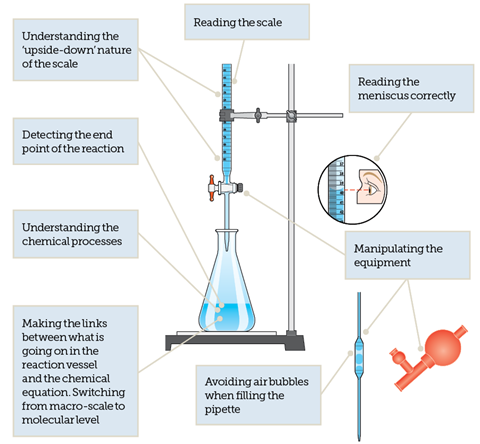
Moles And Titrations Cpd Rsc Education
A known amount of both products is used to determine the amount of reactant.
. It is a must for physical chemistry laboratory experiments. In this topic we will certainly. A quantitative and volumetric technique to determine the unknown concentration of a solution by the known concentration of a solution in the presence of indicator is called Titration.
What is the purpose for using phenolphthalein for an acid base titration. Titration It is also known as titrimetry and volumetric analysis 1. Which definition best describes a titration.
Titration is a common laboratory method of using quantitative chemical analysis. Titration is a process or method to determine the concentration of a substance in a solution in which a known reagent is added to a solution of unknown concentration. The process of carrying out a titration allows us to accurately measure the volumes of an acid and an alkali required for neutralisation.
It is used in quantitative analytical chemistry to determine an. Tap card to see definition. Carefully measured amounts of the reagent are added until a change in color or.
Combining two reactants to form a product and measuring the amount of that product against the theoretical yield. In a strong acid-weak base titration the pH is less than 7 at the equivalence point. A titration is a technique where a solution of known concentration is used to determine the concentration of an unknown solution.
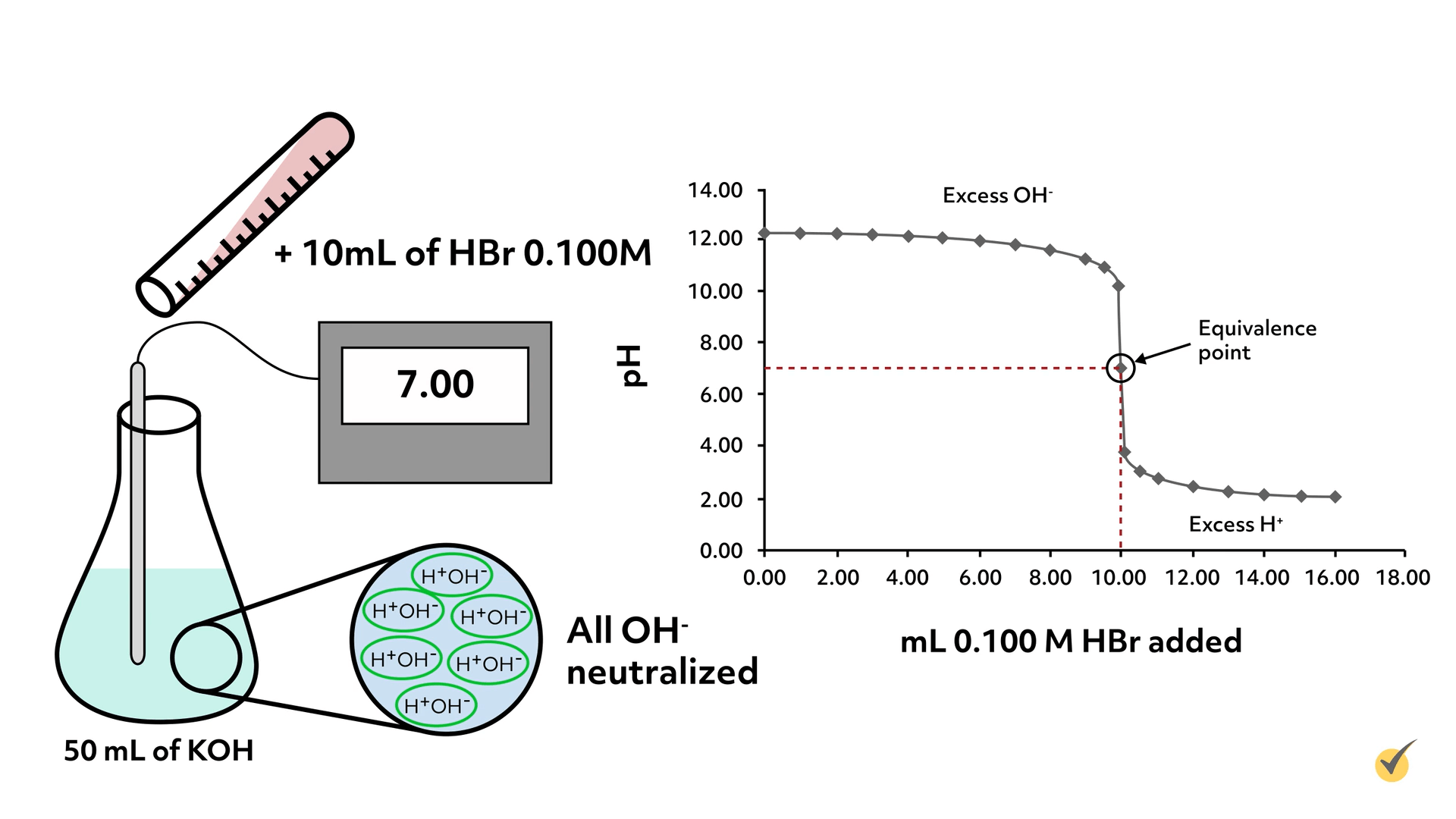
Diagram of solution transformation as titration begins. To use this curve to estimate the pKa values of the ionizable groups of the amino acid. Typically the titrant the know solution is added from a buret to a known quantity of the analyte the unknown solution until the reaction is complete.
Titration which is also known as titrimetry is a chemical qualitative analysis technique that is used to calculate the concentration of a given analyte in a mixture. A a technique used to determine the chemical identity of an unknown. The Titration Curve.
To prevent an undesired change in a variable. She adds a base from a burette to an acid. She continues to.
B a type of chemical reaction used to identify the stoichiometric relationship between two reactants. The general shape of the titration curve is the same but the pH at the equivalence point is different. Which of the following best describes a titration.
To determine the titration curve for an amino acid. Furthermore there are four important types of titration. The purpose of the titration is the detection of the equivalence point the point at which chemically equivalent amounts of the reactants have been mixed.
To determine the end point of titration. Click again to see term. The volume measurement is.
A known amount of one reactant is used to determine the amount of another reactant. To understand the acid base behaviour of an amino acid. This is the pH recorded at a time point just before complete neutralization takes place.
Maya a student performs a titration. She cleans and rinses a burette with base solution. Titration is the process in which one solution is added to another solution such that it reacts under conditions in which the added volume may be accurately measured.
It works by gradually combining a base of known concentration with an unknown acid solution or vice versa until the solution is neutralized. C a method for determining the concentration of a solution. The titration curve is a graph of the volume of titrant or in our case the volume of strong base plotted against the pH.
Acid solution of known concentration required to neutralize it. In a weak acid-strong base titration the pH is greater than 7 at the equivalence point. First of all titration is an important part of the study of chemistry.
The amount of reactants that have been mixed at the equivalence point depends on the stoichiometry of the reaction. This method is used to determine the unidentified concentration of a known analyte. She observes a color change in the Erlenmeyer flask.
A method for determining the unknown concentration of a solution using the known concentration of another solution. To make sure the results of the experiment support the hypothesis. She fills the burette with standardized base solution.
To examine whether one variable causes a change in another. Titration curve of weak acid and strong base. There are several characteristics that are seen in all titration curves of a weak acid with a strong base.
To prevent a dangerous condition resulting from a reaction. Titration curves are obtained when the pH of given volume of a sample solution varies after successive addition of acid or alkali. Knowing the volume of titrant added allows the determination of the concentration of the.
Click card to see definition. Titration refers to a process where the use of a solution of known concentration takes place for the determination of the concentration of an unknown solution. At this point moles of NH added moles of HCl in the analyte.
A titration is an experiment where a volume of a solution of known concentration is added to a volume of another solution in order to determine its concentration. This is the equivalence point halfway up the steep curve. Titration process of chemical analysis in which the quantity of some constituent of a sample is determined by adding to the measured sample an exactly known quantity of another substance with which the desired constituent reacts in a definite known proportion.
Titration is an important technique in the field of analytical chemistry and is sometimes referred to as volumetric analysis also. The point at which neutralization occurs is called the equivalence point and is often indicated by a. Many titrations are acid-base neutralization reactions though other types of titrations can also be performed.
Titration is defined as a method or process of determining the concentration of a dissolved substance in terms of the smallest amount of reagent of known concentration required to bring about a given effect in reaction with a known volume of the test solution.

Titration Curves Equivalence Point Article Khan Academy

0 Comments